How to Verify Legitimate Website Proof in 2026
That padlock icon in your browser? It only means your connection is encrypted. It says nothing about whether the business behind the site is honest, how they use your data, or whether their AI practices are transparent.

Proving a website is legitimate now requires looking beyond security markers. This guide covers the verification steps, tools, and trust signals that separate trustworthy sites from convincing fakes, including the newer AI transparency certifications that traditional checks miss entirely.
What makes a website legitimate
A legitimate website typically displays a valid SSL certificate (the padlock icon in your browser), transparent contact information, clear privacy policies, verifiable business registration, and authentic customer reviews from multiple sources. Yet legitimacy extends beyond security markers alone.
True website legitimacy means the business behind the site operates honestly. This includes how they handle your data, how they use AI in their operations, and whether their claims can be independently verified by a third party.
Here's the distinction worth understanding: a secure connection protects your information during transfer, but it reveals nothing about the company's actual business practices. Scammers can obtain SSL certificates just as easily as legitimate businesses. The real question is whether you can trust the organization itself, not just the technology protecting your connection.
How to check if a website is legit
Before buying from an unfamiliar site or sharing personal information, running through a few verification steps can reveal different aspects of a website's trustworthiness.
1. Run a free website safety scan
Free website legitimacy checker tools scan sites against databases of known scams, malware, and blocklists. URLVoid, for instance, checks a site against over 30 security engines at once. Google Safe Browsing flags sites that host malicious content or engage in phishing attempts.
Running a scan takes seconds and catches obvious red flags. If a site appears on multiple blocklists, that's a clear warning sign worth paying attention to.
2. Verify SSL certificates and secure connections
The padlock icon in your browser's address bar and a URL starting with "https" indicate an encrypted connection. Clicking the padlock reveals certificate details, including who issued it and when it expires.
Here's the catch, though: SSL certificates are cheap and easy to obtain. A padlock alone doesn't prove legitimacy. It only means your connection is encrypted. Scammers know this and frequently use valid certificates to appear trustworthy (over 90% of phishing sites displayed the padlock icon in 2023), so the padlock is just a starting point.
3. Research domain age and ownership details
WHOIS lookup tools reveal when a domain was registered and who owns it. ICANN Lookup and Whois.com both offer free searches that take just a few seconds.
Brand-new domains with hidden ownership details are red flags. Legitimate businesses typically register domains for multiple years and display accurate contact information. A site claiming to be an established company but registered last month deserves extra scrutiny before you trust it with your information.
4. Look for verified third-party certifications
Anyone can paste a trust badge image onto their website. The difference between real and fake certifications comes down to verification.
Clickable badges: Real certifications link to the issuing organization's verification page
Public registries: Some certifications can be independently confirmed through searchable databases
Self-claimed badges: Images without verification links mean nothing
Click any trust seal to confirm it connects to a legitimate verification page. Better yet, look for certifications listed in public registries where you can independently confirm a company's status without relying on the company's own website.
5. Check customer reviews and trust ratings
Reviews displayed on a website can be curated or fabricated, so cross-referencing reviews across multiple platforms like Trustpilot, Google Reviews, and the Better Business Bureau provides a more complete picture.
Watch for patterns that indicate fake reviews: generic language, clusters of five-star ratings posted on the same day, or reviewers with no other review history. With 30% of online reviews considered fake or inauthentic, these warning signs matter.
Best website legitimacy checker tools
Different tools verify different aspects of legitimacy. Understanding what each type checks helps you choose the right tool for your situation.
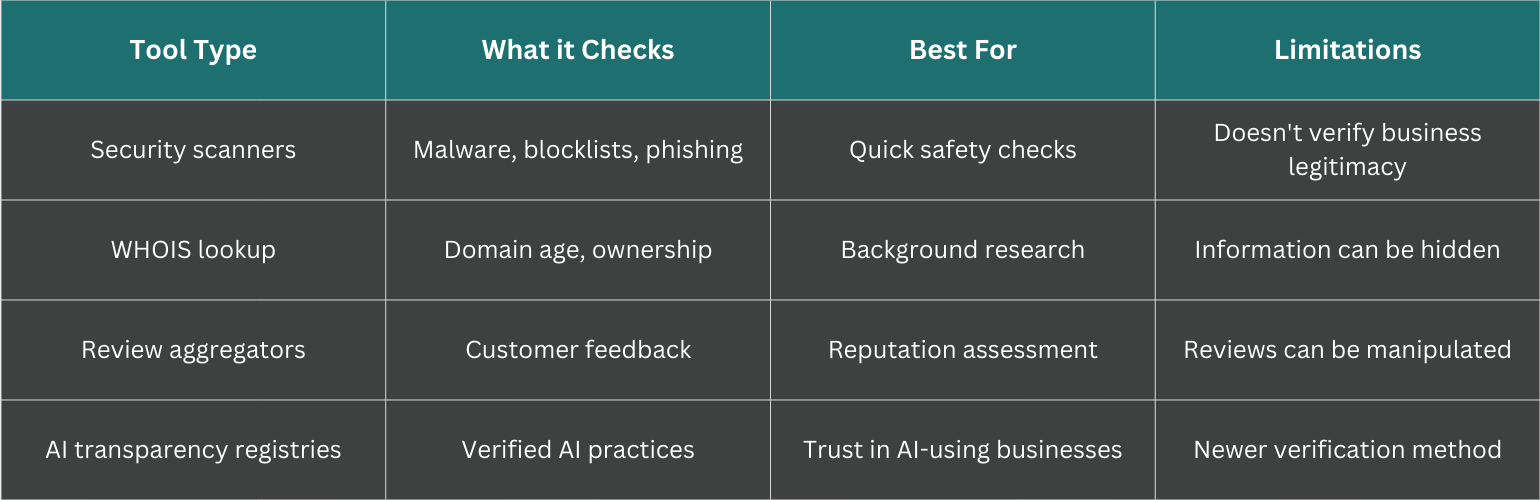
Free security scanners and malware detectors
URLVoid, VirusTotal, and Google Safe Browsing all offer free scans that check whether a site hosts malware or appears on security blocklists. These tools excel at catching technical threats, though they won't tell you if a business is honest. They will, however, flag sites that could harm your device.
Domain lookup and WHOIS verification tools
ICANN Lookup provides official domain registration data, while Whois.com offers a more user-friendly interface for the same information. Look for registration dates, registrant contact details, and how long the domain is registered. Legitimate businesses typically don't hide this information from public view.
Review aggregators and reputation platforms
Trustpilot aggregates customer reviews across thousands of businesses. The Better Business Bureau tracks complaints and business responses over time.
The most useful signal isn't always the overall rating. How a company responds to negative reviews often reveals more about their legitimacy than a perfect score. Legitimate businesses address complaints professionally and work to resolve issues publicly.
AI transparency verification registries
As AI becomes embedded in business operations, a new type of verification has emerged. Public registries now allow consumers to check whether a company has been independently certified for transparent AI practices.
SiteTrust maintains a public registry where anyone can verify a company's AI transparency certification before doing business with them. This addresses a gap that traditional security tools don't cover, specifically how companies use AI and whether they're honest about it.
Signs that prove a website is trustworthy
Valid SSL certificate: Confirms encrypted connection, though not business legitimacy on its own
Complete contact information: Real address, phone number, and responsive email that you can verify
Clear policies: Accessible privacy policy, return policy, and terms of service written in plain language
Verified reviews: Authentic customer feedback across multiple platforms, not just the company's own site
Clickable certifications: Trust seals that link to verification pages where you can confirm their validity
AI and data transparency: Clear disclosures about how the company uses AI and handles customer data
The last point is increasingly important as AI touches more business decisions. Consumers want to know whether AI influences the products, prices, or recommendations they see.
Why traditional website checks are no longer enough
Security scans and SSL verification tell you whether a site is technically safe. They don't tell you how a company uses your data or whether AI influences your experience on their site.
Consumer skepticism about AI is growing, with only 17% having full trust in organizations managing their identity data. People want to know: Is AI making decisions about me? How is my data being used? Is this company being honest about their practices? Traditional website checks can't answer any of these questions.
AI transparency has become the new frontier of proving website legitimacy. A company can pass every security scan while still using AI in ways that affect customers without their knowledge. This gap between technical security and operational transparency is where trust breaks down.
How AI transparency certification proves website legitimacy
Independent certification adds a layer of proof that goes beyond security. It verifies that a business operates transparently in how they use AI, not just that their website is technically secure.
What AI transparency certification evaluates
Certification examines a company's AI policies, data practices, and disclosure standards. Evaluators assess whether the organization clearly communicates how AI affects customers and whether their practices match their public claims.
This isn't a self-assessment where companies grade themselves. Independent certification means a third party has verified the company's transparency practices against established standards.
How public registries let consumers verify trust
Public registries create accountability that self-claimed badges cannot provide. Anyone can look up a company's certification status before making a purchase or sharing personal information.
SiteTrust's registry lists all certified organizations publicly, transforming trust from a claim into verifiable proof. Rather than taking a company's word for it, consumers can confirm certification status independently.
Meeting compliance for upcoming AI regulations
The EU AI Act and Colorado AI Act are introducing new transparency requirements for businesses using AI. Companies that certify now position themselves ahead of regulatory requirements rather than scrambling to comply later.
Early certification signals to customers that a business takes transparency seriously because they choose to, not because they're forced to. This distinction matters to consumers who are increasingly aware of AI's role in their daily interactions with businesses.
How businesses prove their website is legitimate
For business owners, demonstrating legitimacy to skeptical visitors requires more than technical security measures.
Display independently verified certifications
Third-party verification carries more weight than self-claimed badges because customers can confirm it independently. Certifications that customers can verify through public registries or issuer websites build more trust than images that could be copied from anywhere.
Publish clear AI and data use policies
Explaining how you use AI in plain language helps customers understand what to expect. Describing what data you collect, how you use it, and how AI influences customer experiences addresses the questions that traditional privacy policies often leave unanswered.
Get listed in public trust verification registries
Public listing creates proof that anyone can check without relying on your word alone. For businesses using AI, SiteTrust certification provides this verifiable trust signal through a searchable public registry.
Ready to prove your website's legitimacy? Get certified for AI transparency with SiteTrust
Turn website legitimacy into customer confidence
For consumers, verification steps help identify trustworthy sites before sharing personal information or making purchases. For businesses, verified transparency converts skeptical visitors into confident customers who feel informed about how their data is used.
Trust is a competitive advantage in a marketplace where consumers have more choices than ever. The companies that prove their legitimacy, rather than just claiming it, win more customers and build lasting loyalty.
Get certified for AI transparency with SiteTrust
FAQs about website legitimacy verification
Is a padlock icon enough to prove a website is safe?
No. The padlock only shows your connection is encrypted. It doesn't verify that the business behind the site is legitimate or trustworthy. Scammers frequently use valid SSL certificates to appear legitimate.
Can scam websites have valid SSL certificates?
Yes. SSL certificates are inexpensive and easy to obtain from certificate authorities. Many fraudulent sites display the padlock icon while running scams, which is why verifying legitimacy through multiple methods matters.
What is the difference between website security and website legitimacy?
Website security means your data is encrypted during transfer between your browser and the server. Website legitimacy means the business itself operates honestly and transparently. A site can be technically secure but still run by scammers.
Do trust badges actually guarantee a website is legitimate?
Only if you can click the badge and verify it through the issuing organization. Fake badges are just images anyone can copy and paste onto their site. Always click to confirm certification is real before trusting it.
How do I report a website I think is a scam?
Report suspicious sites to the FTC at ReportFraud.ftc.gov. You can also report to Google Safe Browsing through their transparency report, your browser's security team, and the website legitimacy checker tools you used during your verification process.
Ready to become a founding member?
Apply for certification todayStay ahead on AI transparency
Join the SiteTrust newsletter to receive updates on AI transparency, new regulations, and practical guides straight to your inbox.
